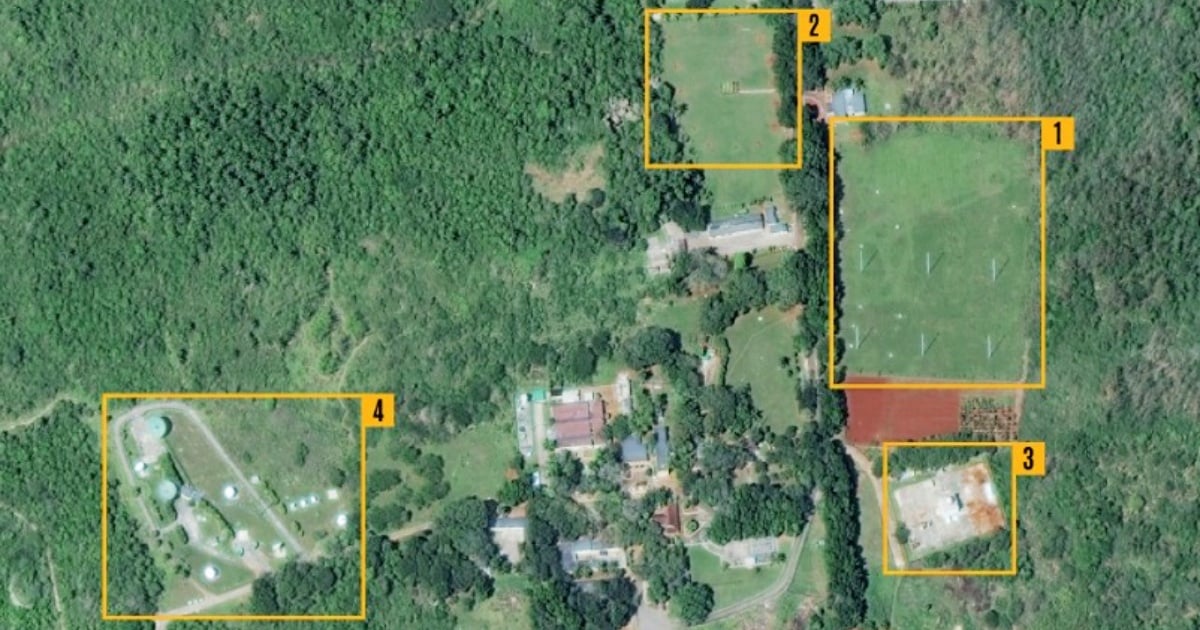
The United States has uncovered at least a dozen Chinese facilities in Cuba, potentially being utilized by the Chinese regime to gather intelligence in the region. According to a report by the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), based on satellite imagery and other intelligence sources, four of these locations play a crucial role in intercepting sensitive communications and monitoring strategic activities.
These bases have been pinpointed in Bejucal (Mayabeque), Wajay and Calabazar (Havana), and El Salao (Santiago de Cuba). The report suggests these sites are equipped with advanced signal intelligence (SIGINT) technology and exhibit physical features typical of espionage purposes, such as sophisticated antennas, perimeter fencing, and a military presence.
Chinese-Cuban Relations: A Growing Partnership
For decades, the ties between China and Cuba have been marked by increasing economic, political, and strategic cooperation. However, recent investigations by the CSIS have shed new light on the extent of this relationship, indicating the possible presence of Chinese-operated intelligence facilities in Cuba. These findings, based on satellite image analysis and open-source information, suggest that Beijing has significantly expanded its intelligence-gathering capabilities in the Caribbean, just a short distance from the United States.
For years, rumors of Chinese intelligence presence on the island were sporadic and lacked official confirmation. Yet in June 2023, officials from the Biden administration acknowledged that China had access to espionage facilities in Cuba. This admission, followed by reports identifying up to four potential sites, represents a turning point in evaluating Cuba's strategic role amidst global power competition.
The Strategic Importance of Cuba
Located less than 100 miles from Florida's coast, Cuba offers a unique strategic position for gathering signal intelligence (SIGINT). The southern United States hosts significant military infrastructure, including command centers, space launch facilities, and naval bases. For China, a SIGINT presence on the island is an invaluable opportunity to monitor sensitive communications, military activities, and U.S. aerospace operations. Additionally, controlling strategic information in the Caribbean could give Beijing a considerable advantage in a global competition scenario.
The Cuban facilities also facilitate the interception of satellite data and telecommunications networks, areas of particular interest to Chinese intelligence.
Identified Facilities
The CSIS investigation identified four sites in Cuba with features suggesting their use for SIGINT collection:
BEJUCAL: This historic complex, known for its role in the 1962 Missile Crisis, remains a nerve center of intelligence. Satellite images reveal an active and modernized infrastructure, including parabolic antennas aimed at geostationary satellites. Its proximity to the Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Space Force Station allows China to monitor space launches and gather critical data on advanced U.S. technologies.
EL SALAO: Near Santiago de Cuba, this new site has been under construction since 2021. Equipped with advanced high-frequency direction-finding (HFDF) systems, it can track radio signals over thousands of miles. The connection of this project with Chinese investments in local infrastructure, like the Moncada Cement Plant, reinforces the possibility of strategic objectives.
WAJAY: Less than 10 kilometers from Bejucal, this smaller facility has shown signs of constant expansion over the past 20 years. Currently, the site hosts 12 antennas of various sizes, as well as operations facilities and a small solar park ensuring energy in case of failures in the Cuban power system. With a dozen antennas, a solar park, and security measures, it seems designed to intercept terrestrial signals and conduct diversified SIGINT missions. While the CSIS acknowledges no parabolic antennas at this site, suggesting a focus on intercepting terrestrial signals, documents mention potential Chinese involvement in its construction or modernization.
CALABAZAR: Although less documented, this base is equipped with modern gear to track satellites and gather space intelligence. In Calabazar, the report highlights recent improvements, such as the construction of a large solar park initiated in 2012, and the presence of parabolic and vertical antennas oriented south. While no public records link this base to China, Cuban defectors cited by the CSIS consider it part of intelligence efforts on the island. According to the study, the equipment in Calabazar could serve to monitor satellites in geostationary orbit, providing China with advanced capabilities to track its space assets and activities of other nations, including the United States.
China's SIGINT Strategy
Signal intelligence is a cornerstone of modern espionage capabilities. It enables the interception of communications and tracking of military movements, providing a crucial advantage in analyzing adversaries and competitors. Despite advances in data encryption, monitoring radio frequency and satellite signals remains valuable for collecting tactical and strategic information. For China, expanding its SIGINT capabilities beyond its borders, especially in a location so close to the U.S., reinforces its ambition to become a dominant global player. Data gathered from Cuba could complement the technological capabilities of the People's Liberation Army, offering Beijing a unique perspective on Washington's military and security activities in the Western Hemisphere.
Cuba's Economic Crisis: An Opportunity for Beijing
The growing influence of China in Cuba is closely linked to the island's ongoing economic crisis. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, Cuba's economy has suffered a severe contraction, with rampant inflation, fuel shortages, and a massive exodus of citizens. In this context, China's financial and technological assistance has been crucial for the Havana government. Beijing has financed infrastructure projects, including the port of Santiago de Cuba and solar parks, and provided telecommunications technology through companies like Huawei and ZTE. These initiatives not only strengthen bilateral ties but also position China as an indispensable partner for Cuba amid its economic isolation.
The presence of China in Cuba poses significant challenges for regional security and strategic stability. The United States now faces a situation where a global adversary has access to intelligence facilities less than 100 miles from its borders. This scenario recalls the importance of Cuba during the Cold War when it was a key point in the rivalry between Washington and Moscow. Additionally, the strengthening of cooperation between China and Cuba could extend beyond SIGINT, encompassing human intelligence (HUMINT) and other forms of espionage. The history of Cuban intelligence, with a sophisticated network focused on the U.S., suggests that Havana could share critical information with Beijing, further expanding Chinese capabilities.
Understanding China's Intelligence Operations in Cuba
What is the significance of the Chinese intelligence facilities in Cuba?
The Chinese intelligence facilities in Cuba allow China to monitor U.S. communications, military activities, and aerospace operations, providing a strategic advantage in global competition.
How has China's presence in Cuba affected regional security?
China's presence in Cuba poses significant challenges for regional security, as it gives China access to intelligence facilities near U.S. borders, reminiscent of Cold War tensions.
Why is SIGINT important in modern espionage?
SIGINT is crucial in modern espionage because it allows the interception of communications and tracking of military movements, offering a significant advantage in analyzing adversaries.
How has Cuba's economic crisis benefited China's influence?
Cuba's economic crisis has allowed China to increase its influence by providing financial and technological assistance, making it an essential partner for Cuba amid its economic struggles.